Custom HTML
All text elements within a screen (header, description, footer), a page (header, description, footer), and a block (title, subtitle, description, footnote) support custom HTML, enabling a wide range of customization:
- Enhanced Formatting: Modify font size, color, or add emphasis using HTML tags.
- Embedding Media: Incorporate images, videos, or audio files to enrich the user experience.
- Interactive Elements: Add links to privacy statements or cookie policies.
SurveyCompo uses specific 'html' keys for custom content:
htmlHeaderhtmlDescriptionhtmlFooterhtmlTitlehtmlSubtitlehtmlFootnote
For a detailed list of keys applicable to screens, pages, and blocks, please refer to the Data Models section in the documentation.
Warning
Ensure that you use correct HTML syntax and prioritize security. Be cautious not to include code from untrusted sources or user input, as it could potentially introduce security risks.
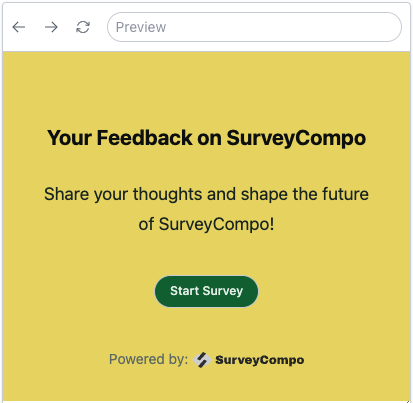
The following example demonstrates how to use HTML to add a logo to the start screen:
{
/* ... */
"css": "#mylogo { width: 10em; display: inline; color: red}",
"startScreens": [
{
"header": "Your Feedback on SurveyCompo",
"description": "Share your thoughts and shape the future of SurveyCompo!",
"okButtonLabel": "Start Survey",
"htmlFooter": "Powered by: <img id='mylogo' onclick=\"alert('SurveyCompo Rocks!')\" src='https://www.surveycompo.com/logos/title-dark.min.svg' />"
}
]
}
Tip: Applying CSS to Custom HTML Elements
You can apply CSS rules to custom HTML elements using the css key or <style> tag. For instance, assign an id attribute to your custom HTML element and reference it in the CSS rules to apply custom styles.
Tip: Invoking JavaScript Functions from Custom HTML Elements
You can invoke JavaScript functions from custom HTML elements using HTML event attributes such as onclick. This enables you to trigger custom actions when users interact with the survey. However, ensure that the JavaScript functions are defined on the hosting page or are accessible to the survey.
Note
For security reasons and to prevent potential vulnerabilities, <script> tags in custom HTML are not evaluated.